General study of Secure E-commerce Logistics Distribution
RuiFUa, Mohammed AbdulhakimAl-Absia, AhmedAbdulhakim Al-Absib, MangalSainc,
Hoon Jae Leec
aDepartment of Ubiquitous IT, Graduate School, Dongseo University, 47 Jurye-ro, Sasang-gu, Busan 47011,Republic of Korea
bDepartment of Smart Computing, Kyungdong University 46 4-gil, Bongpo, Gosung, Gangwon-do,
24764, Republic of Korea
c Division of Information and Communication Engineering, Dongseo University, 47 Jurye-ro, Sasang-gu, Busan 47011, Republic of Korea
furui.qilianteng@gmail.com, Mohammed.a.absi@gmail.com, absiahmed@kduniv.ac.kr, mangalsain1@gmail.com, hjlee@dongseo.ac.kr
Abstract
E-commerce logistics distribution refers to the enterprise adopts networked computer technology and advanced management methods. The activities and processes are passed to the user and according to the user's order requirements, which it conducts a series of record, sorting, and determines the quantity of goods according to the agreed time and place. This new type of logistics distribution model has brought about tremendous changes in the field of circulation. This paper presented a General study of E-commerce logistics distribution.
Keywords: e-mcommerce, e-commerce logistic, e-commerce logistic distribution.
1. Introduction
In the traditional logistics distribution, there are unreasonable factors such as low automation, untimely information reception, and low network level, which hinders the efficiency of logistics distribution. The logistics distribution under e-commerce is a new logistics distribution mode that can shorten the distribution cycle, optimize the service quality and improve the competitiveness of enterprises by combining information network technology and logistics distribution in an open network environment. This kind of distribution mode is conducive to the improvement of logistics distribution efficiency. Logistics distribution under the e-commerce environment has many characteristics such as a large number of customers, relatively small customer demand, obvious customer dispersibility, and time requirements.
The rapid development of [1] information, communication, and network technologies has accelerated the pace of economic globalization and integration. because of the rapid life cycle, competition of enterprises is increasing where the personalization and diversification of customer needs becoming more and more obvious. It is difficult for traditional business models to cope with changing market demandsTherefore, the business model of the company must be fast conform to these changes. E-commerce is generally based on an open Internet environment, browsers/servers and other applications. For instance, buyers and sellers do not meet each other and carry out various business activities. However, E-commerce can be divided into broad e-commerce and narrow sense E-commerce. Using electronic services to achieve business, generalized e-commerce can be done through the intranet, extranet, and electronic tools for instance, Internet that share information between companies, suppliers and customers . Narrow e-commerce is to complete various trading activities through computer networks. E-commerce system consists of six Composition:, e-commerce customers, online store, certification center, online banking, logistics, and network system. Logistics refers to the physical movement of a physical entity from a supplier to a demander. It is created by a series.
The composition of economic activity of time value and spatial value. Including order processing, purchase purchase, purchase warehousing, inventoryManagement, distribution replenishment, distribution processing, distribution operations, financial operations and many other basic activities. Logistics system is a system that controls raw materials, finished goods, finished goods, and information [2].
2. Main service functions of logistics
The main service functions of logistics are reflected in the following aspects:
1) Transportation function.
2) Custody function.
3) Delivery function.
4) Loading and unloading function.
5) Packaging function.
6) Logistics processing function.
7) Information processing function.
Distribution is a form of logistics. From the perspective of the way of circulation of goods, logistics and distribution is a modern. The way goods are circulated the whole process of logistics and distribution includes the following basic steps:
1) Formation of logistics orders: Customers submit orders via network devices such as the Internet, and customer service centers receive
The customer's order is sorted and summarized, and the personnel are arranged to pick up the goods.
2) Prepare the goods: The preparation for the distribution is to collect the items to be distributed from various distribution points.There is a distribution center for stock distribution.
3) Sorting and distribution: The sorting and distribution process can be divided into several separate processes, including the outbound document review nuclear, outbound information processing, picking, distribution, and outbound inspection.
4) Processing and fitting: It is an extension of circulation processing activities, such as bulk filling operations and repackaging of finished goods. The purpose is to improve the level of logistics services and reduce logistics costs.
The basic goal of logistics and distribution is to reduce logistics costs as much as possible while meeting the needs cut the costs [3].
2. Characteristics of E-commerce logistics distribution
E-commerce logistics and distribution is to meet the customer's satisfaction, and it is the basic goal of the enterprise to find ways to minimize the transportation cost during the operation [5][6]. Characteristicsof E-commerce logistics distribution are a large number of customers, size of each customer's demand is relatively small, dispersion of customers is obvious, customer has high requirements for the timeliness of arrival of the goods, high customer service needs, and Suppliers strive to save costs.Fig.1.

Fig. 1 Characteristics of E-commerce logistics distribution
3. Different types of E-commerce logistics distribution
In Fig. 2, third-party logistics refers to a form of logistics in which a professional enterprise other than the consignor and consignee related to the goods, that is, a third party, undertakes the logistics activities of the enterprise. The third-party logistics provider is defined as “a company that determines the return by contract and assumes all or part of the logistics activities of the owner. The service forms provided can be divided into operations-related services, management-related services, and both. There are three types of services, etc. Any form must be higher than the services provided by the past common carrier and contract carrier.
Constructed a third-party logistics and enterprise interest alliance: In summary, third-party logistics is a personalized series of logistics services provided by third-party logistics providers to users at specific prices for a specific period of time, and jointly builds alliances between enterprises.
First, third-party logistics is a contract-oriented set of services. Third-party logistics is different from traditional outsourcing. The outsourcing is limited to one or a series of decentralized logistics functions, such as transportation companies providing transportation services, warehousing companies providing warehousing services, and third-party logistics according to the requirements of the contract terms. It is not a temporary demand, providing versatile and even comprehensive logistics services. In accordance with international practice, the service provider charges 20% of the gross profit of the demand side during the contract period.
Second, third-party logistics is an alliance between enterprises. The third-party logistics companies share information fully, which requires the two parties to trust each other to achieve better results than the logistics activities alone. Moreover, from the perspective of the logistics service provider’s charging principle, It is to share the risks and share the benefits; in addition, the relationship between the enterprises is not only one or two market transactions, but after the transaction has been maintained for a certain period of time, the transaction objects can be replaced with each other [4]. Take the behavior that maximizes the self-interest, and do not take the behavior that maximizes the common interest. Only in the logistics aspect, the contract is formed into an intermediate organization with equal advantages, risk sharing, two-way or multi-directional flow. Therefore, the enterprise There is a logistics alliance relationship.
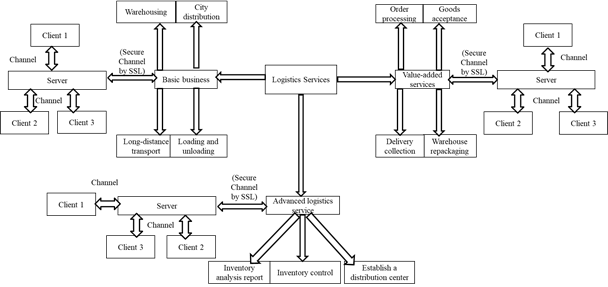
Fig. 2 Secure E-commerce logistics distribution
Saving costs is equal to creating profits: The demand for high-quality logistics services by SMEs is very urgent. Especially in foreign trade, small and medium-sized foreign trade enterprises have been striving to find safe, efficient and low-cost logistics services. A single enterprise is limited to its own business scale. In the process of using third-party logistics, it does not reduce the cost for the enterprise. Similarly, because of the low profit, the logistics demand of small and medium-sized enterprises is not attractive to third-party logistics companies. The total logistics demand of SMEs is huge, but they are scattered. If a large number of SME logistics needs can be integrated and packaged, and then connected to third-party logistics, it can save a lot of costs and create huge profits, and promote the overall development of the logistics industry service level. So who is going to integrate these huge but scattered logistics needs? B2B e-commerce platform is increasingly equipped with this integration capability. Users on the platform will have logistics service needs as long as there is a transaction, and the platform will classify the data. Organize the package and open the data to third-party logistics. SMEs get the most cost-effective logistics services through the B2B e-commerce platform, and third-party logistics gains huge profits due to long-term continuous large-scale demand. The B2B platform thus gains user stickiness and expands the platform advantage.
Third-party logistics is an important form of logistics specialization. When the logistics industry develops to a certain stage, third-party logistics will inevitably occur, and there is a very close correlation between the third-party logistics market share and the logistics industry. At present, China's logistics level is still in its infancy, and both third-party logistics companies and B2B e-commerce platforms will have great potential to participate in them, and they will certainly face these huge challenges.
IBUonline Global Business Alliance: It has become an important network channel for global buyer procurement and suppliers and service providers. He has utilized the world's most advanced open cloud computing technology and has opened up a combination of third-party and upstream and downstream supply chain services including logistics, ports and information. The platform not only accurately matches and matches the purchase data of international buyers with the production data of the production enterprises, but also optimizes and integrates the information, finance, logistics, port and other services between upstream and downstream on the platform and conducts one-stop operation. Online trading solves problems such as market, order trading, service and supply chain.
Secure Sockets layer (SSL), provide the security when we transmit the information on the internet. However, when the client use the browser, SSL will establishsecure link among the client and the server browser. Encrypt messages among the web server and the web browsers we use the Secure Sockets layer (SSL) where it encrypt the data packets of the Transport layer. One of the large problems of SSL is that dealer can stock the sensitive data of the cardholder where the protocol does not deny the non-repudiation due to the client authentication optional.
4. Conclusion
E-commerce logistics and distribution is to meet the customer's satisfaction, and it is the basic goal of the enterprise to find ways to minimize the transportation cost during the operation. In this paper we perused the concept of Main service functions of logistics, general study of E-commerce logistics distribution. Different types of E-commerce logistics distribution.Therefore, the future work would consider the issues and challenges of E-commerce logistics and distribution
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the Technological Innovation R&D Program (Assignment number: S2457495) funded by the Small and Medium Business Administration (SMBA, Korea).
References
[1] Dantzig G,Ramser J.The truck dispatching problem[J],Management Science,1959,6:80-91.
[2] Li Junn, Guo Yaohuang,” Logistics Distribution: Theory and Method of Vehicle Optimization Scheduling Beijing: China Materials Press. 2006.
[3] Wang Xiaobo, Li Jun. Research on Optimization of Logistics Distribution Routing in E-commerce [J], Computer Engineering, 2007, 33(10): 202-210.
[4] Eilon S,Christofides N.Distribution management:mathematical modeling and practical
Analysis [M],London:Griffin,1971
[5] Li Weijian. Research on logistics distribution route optimization under B2C e-commerce mode [D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University. 2007.
[6] Ding Liyan, Zhang Wei. Logistics Foundation [M], Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2000, 78-79.